SYNCHRONOUS ULTRASOUND PARALLEL BEAMS: MECHANISM AND EFFICACY FOR ACNE SCARS
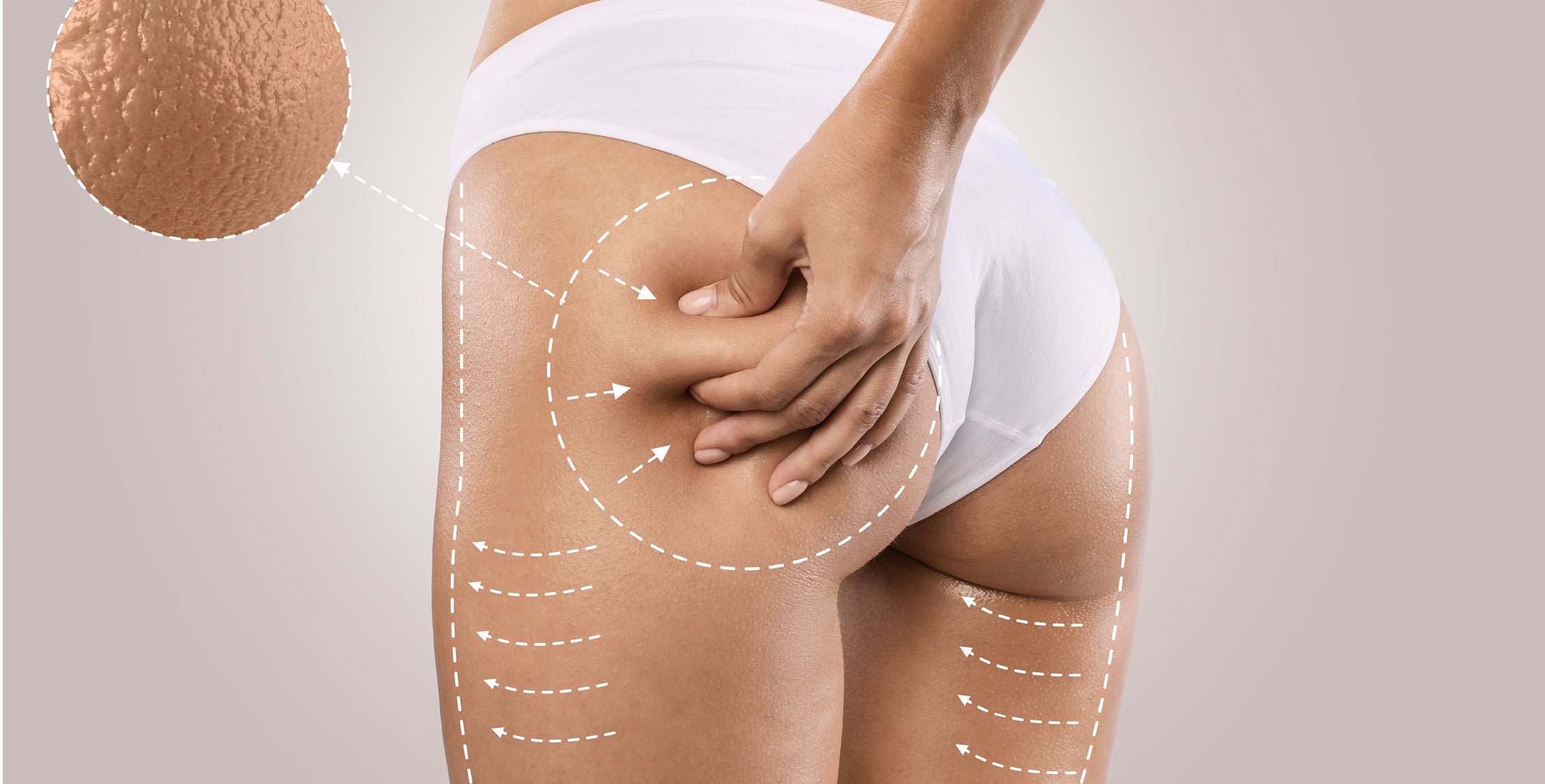
Acne scars are notoriously difficult to treat, requiring deep dermal action while minimizing the risk of complications and downtime, especially in patients with darker skin types. A recent study in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology describes Synchronous Ultrasound Parallel Beam (SUPERB) technology: high-intensity, high-frequency, non-focused ultrasound creates multiple "cylindrical" zones of controlled thermal injury (approx. 60–70°C) in the mid-dermis. The epidermis is preserved through integrated cooling and real-time skin temperature monitoring. The authors retrospectively evaluated the results of a single treatment for acne scars: 3D analysis showed an average reduction in depression volume of 23–27%, with moderate pain and no reported adverse events. Full study breakdown and practical insights are provided in our editorial note.